Invest in yourself before you invest in the Market
October 1, 2024
WHAT IS THE MARKET MAKER METHOD
October 1, 2024Advanced Price Action in Forex: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to Forex trading, price action is one of the most reliable strategies used by both beginners and experienced traders alike. However, to truly master price action trading, one must go beyond basic chart patterns and understand the market’s underlying dynamics. Advanced price action is where traders focus on the actual buying and selling pressures that drive the market.
This guide will delve into advanced price action techniques and provide insights into the key factors influencing market movements. We’ll also explore important concepts such as support and resistance, impulse and corrective moves, and more.
Introduction to Advanced Price Action
Price action trading revolves around analyzing historical price movements to make trading decisions. But what distinguishes advanced price action from its basic counterpart is the understanding of what really moves the market: buying and selling pressure.
What Moves the Financial Market?
Contrary to popular belief, it’s not simply the number of buyers versus sellers that move the price. Instead, it’s the pressure that these buyers and sellers exert on the market. Let’s break it down:
Imagine you want to sell 1 million shares of a stock like “ZagaTech Company.” At the same time, there are 10 buyers, each looking to purchase 100 shares. Despite having more buyers than sellers, your large sell order creates selling pressure that outweighs the smaller buy orders. This causes the price to move lower.
The takeaway here is that price rises when there’s more buying pressure than selling pressure and falls when selling pressure exceeds buying pressure. Understanding this dynamic is key to advanced price action trading.
Key Concepts in Advanced Price Action
Now that we understand the fundamentals of what moves the market, let’s dive deeper into the essential concepts of advanced price action trading. These elements provide the framework for reading and interpreting price charts at a higher level.
1. Support and Resistance
Support and resistance levels are critical to any price action trader’s toolkit. In simple terms, support is a price level where the market tends to find buying interest, preventing the price from falling further. Resistance, on the other hand, is a price level where selling interest tends to emerge, halting the price from rising.
2. Role Reversal in Support and Resistance
In advanced price action, we also encounter the role reversal concept. This occurs when a previous support level, once broken, acts as new resistance, and vice versa. This concept is crucial for identifying potential trade opportunities, as these levels often act as critical decision points for market participants.
3. Dynamic Support and Resistance
In addition to static support and resistance levels, advanced price action also involves dynamic support and resistance, where moving averages or trendlines provide levels of support or resistance. Traders use these dynamic levels to understand the ongoing trend and to place trades in line with the prevailing market direction.
4. Impulse and Corrective Moves
Markets rarely move in straight lines. Instead, they alternate between impulse moves (sharp, strong moves in the direction of the trend) and corrective moves (smaller, counter-trend movements). Understanding this rhythm helps traders enter and exit trades at optimal times. Advanced price action traders look for impulse moves as potential breakout signals, while corrective moves are seen as opportunities to enter a trade at a better price.
Understanding Candlestick Patterns in Advanced Price Action
While traditional price action traders often rely on memorizing dozens of candlestick patterns, advanced traders simplify their approach by focusing on just a few critical elements of the candlestick:
1. The Wick
The wick of the candlestick represents the high and low prices reached during a given period. Long wicks can indicate rejection of certain price levels, often signaling a potential reversal.
2. The Length of the Wick
The length of the wick matters because it shows the extent of market rejection at a certain level. For instance, if a candle has a long upper wick, it suggests that despite higher prices being reached, sellers eventually overpowered buyers, pushing the price back down.
3. The Size of the Body
The body of the candle shows the difference between the opening and closing price. A larger body suggests strong momentum in that direction, while a smaller body may indicate indecision or consolidation.
4. The Close of the Candle
The closing price is particularly important in advanced price action. A close near the high of the candle can signal strong buying pressure, while a close near the low might suggest dominance by sellers.
The Importance of Supply and Demand
Price action trading is closely linked to the principles of supply and demand. In Forex, this means understanding where the major pools of buy and sell orders are located. Key supply zones occur where significant sell orders exist, while demand zones are areas of strong buying interest. Advanced traders focus on these zones to anticipate future price movements.
How to Identify High-Probability Trades Using Price Action
The key to successful advanced price action trading is identifying high-probability trade setups. Here are a few strategies to help you get started:
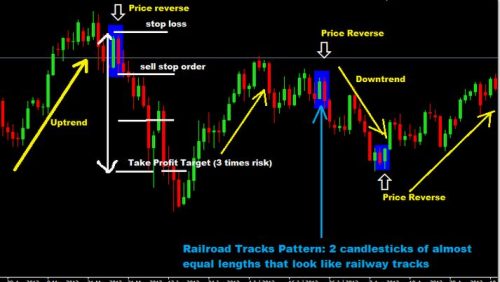
1. Trading Support and Resistance Bounces
One of the most reliable setups involves trading price bounces off significant support or resistance levels. When price reaches a known level of support and starts to reverse upward, this can signal a buying opportunity. Similarly, when price hits a resistance level and begins to fall, it may present a short-selling opportunity.
2. Breakout Trading with Price Action
Another common strategy in advanced price action is trading breakouts. This involves entering a trade when the price breaks through a significant level of support or resistance. To increase the probability of success, look for breakouts that occur during periods of high volatility or when supported by strong volume.
3. Using Impulse and Corrective Waves
As mentioned earlier, price moves in impulses and corrections. Advanced price action traders often wait for the end of a corrective move to enter a trade in the direction of the previous impulse. This strategy helps ensure that you are trading in line with the trend, which increases the chances of success.
Mastering Price Action Psychology
Advanced price action trading isn’t just about reading charts; it’s also about understanding market psychology. Price charts are a reflection of the collective emotions of market participants, including fear, greed, and uncertainty. By recognizing patterns of behavior, such as panic selling or euphoria-driven buying, traders can anticipate market reversals or continuations.
1. Avoiding Emotional Trading
One of the biggest mistakes traders make is letting emotions dictate their decisions. Advanced price action traders develop discipline and stick to their trading plans, avoiding impulsive trades driven by emotions.
2. Reading Sentiment Through Candles
Candlesticks provide a window into market sentiment. A long bullish candle with little to no wick suggests strong buying pressure, while a long bearish candle with little to no wick shows strong selling pressure. By interpreting these candles in the context of support, resistance, and overall market conditions, traders can make informed decisions.
Common Pitfalls in Advanced Price Action Trading
While advanced price action offers powerful insights, it’s not without its challenges. Here are some common mistakes traders make and how to avoid them:
1. Overcomplicating the Analysis
One of the major pitfalls in advanced price action trading is overcomplicating your analysis. Trying to account for too many factors can lead to confusion and indecision. Keep your analysis simple and focus on key levels, market structure, and candlestick behavior.
2. Ignoring Market Context
Every price action pattern must be interpreted within the broader context of the market. For instance, a bullish reversal pattern near a major resistance level might be less reliable if the overall market trend is down. Always consider the bigger picture before making trading decisions.
3. Being Impatient with Trades
Advanced price action trading requires patience. Impulse moves and breakouts don’t happen all the time, so it’s important to wait for the right setups. Entering trades too early or chasing after the market can lead to unnecessary losses.
Conclusion
Advanced price action in Forex trading provides traders with powerful tools to anticipate market movements based on actual buying and selling pressures. By mastering concepts such as support and resistance, impulse and corrective waves, and candlestick analysis, traders can improve their decision-making and achieve consistent success. The key to mastering price action lies in keeping things simple, focusing on high-probability setups, and maintaining discipline throughout the trading process.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between basic and advanced price action?
Basic price action focuses on reading chart patterns, while advanced price action goes deeper by analyzing the underlying buying and selling pressures that drive price movements.
2. How can I identify support and resistance levels?
Support and resistance levels can be identified by looking for areas on the chart where price has previously reversed or consolidated. Advanced traders also use dynamic levels like moving averages.
3. What are impulse and corrective moves in Forex?
Impulse moves are strong price movements in the direction of the trend, while corrective moves are smaller counter-trend movements. Recognizing these helps traders time their entries and exits.
4. Can price action trading be used in all market conditions?
Yes, price action trading can be applied in various market conditions, but it tends to be more effective in trending markets rather than in choppy, sideways markets.
5. What is role reversal in price action trading?
Role reversal refers to when a previous support level becomes resistance after being broken, or when resistance turns into support. It is a key concept in advanced price action analysis.